Top 10 innovations in education
The field of education is undergoing a remarkable transformation with a myriad of innovations reshaping how students learn and educators teach. In this article, we will delve into the top 10 innovations in education, exploring the groundbreaking technologies and methodologies that are revolutionizing the way knowledge is acquired and imparted.
advancements that are redefining healthcare. These innovations hold the promise of transforming patient care, medical research, and the very essence of the healthcare industry, ushering in a new era of possibilities.
Top 10 innovations in education
Immersive Learning

Virtual Reality (VR): Virtual reality is at the forefront of immersive learning. With VR headsets, learners are transported to realistic, computer-generated environments where they can explore, interact, & engage with subject matter. This technology is particularly beneficial for subjects that require hands-on experience, such as medical training or field research.
Augmented Reality (AR): Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the real world, enriching the learning experience. AR apps & devices provide learners with additional context & information, enhancing comprehension in various subjects, from history to engineering.
Gamification: Gamification leverages game elements, such as competition, points, & rewards, to make learning more engaging. Educational games & platforms motivate students to actively participate in lessons, fostering a sense of achievement & accomplishment.
Simulations: Immersive simulations replicate real-world scenarios, allowing learners to practice problem-solving & decision-making in a safe & controlled environment. These simulations are particularly valuable in fields like aviation training & emergency response.
Virtual Laboratories: In STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, & Mathematics) education, virtual laboratories enable students to conduct experiments & explore concepts without the need for physical equipment. This cost-effective approach broadens access to practical learning experiences.
Language Learning Apps: Language learning has been revolutionized by immersive apps that use speech recognition, augmented reality, & virtual conversation partners to immerse users in language practice, accelerating proficiency.
Digital Twins: In fields like engineering & architecture, digital twins create virtual replicas of physical objects or systems. Students can study and manipulate these digital twins, gaining a deep understanding of complex structures & processes.
360-Degree Videos: 360-degree videos offer an immersive perspective, allowing learners to explore different environments or historical sites as if they were there. This technology is widely used in geography & history lessons.
Storytelling in Virtual Worlds: Students can become active participants in historical or fictional narratives by navigating virtual worlds. This approach fosters empathy, critical thinking, & creativity.
Remote and Blended Learning: Immersive technologies have also revolutionized remote & blended learning, offering students a sense of presence & engagement even when they’re not physically present in a classroom.
In conclusion, immersive learning represents a remarkable advancement in education, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge & real-world application. By harnessing the power of immersive technologies, educators are creating dynamic, engaging, & effective learning experiences that are not only more enjoyable but also more conducive to deep understanding & skill development. As these innovations continue to evolve, they hold the potential to make education more inclusive, accessible, & impactful for learners worldwide.
AI in Education
AI in Education: Transforming Learning and Teaching
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful force reshaping the landscape of education, revolutionizing how students learn and teachers instruct. This innovation harnesses the capabilities of machine learning, data analysis, & natural language processing to personalize education, streamline administrative tasks, & enhance overall educational outcomes.
Personalized Learning: AI algorithms analyze individual student performance & tailor learning materials accordingly. Adaptive learning platforms provide custom-tailored lessons and assignments, ensuring that students receive content at their own pace and comprehension level, thus maximizing learning efficiency.
Intelligent Tutoring Systems: AI-powered virtual tutors assist students in mastering subjects. These systems offer real-time feedback, pinpointing areas where students need help & adapting lessons accordingly, fostering a deeper understanding of complex topics.
Smart Content Creation: AI aids educators in generating and curating content. Natural language generation tools can automatically create textbooks, lesson plans, & assessment materials, reducing the time spent on administrative tasks.
Data-Driven Insights: AI processes vast amounts of educational data to identify trends and patterns. Educators can use these insights to improve curriculum design, teaching methods, & student support, leading to more effective learning experiences.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-driven chatbots provide instant support to students and educators, answering questions, offering guidance, & automating administrative tasks. Virtual assistants facilitate communication and coordination within educational institutions.
Grading Automation: AI-powered grading systems streamline the assessment process, providing faster and more consistent feedback to students. Educators can focus on providing personalized guidance instead of manual grading.
Early Intervention: AI can identify students at risk of falling behind, allowing educators to intervene early and provide additional support. This proactive approach helps prevent learning gaps.
Language Translation and Accessibility: AI-driven language translation tools break down language barriers, making education more accessible to non-native speakers. AI can also assist students with disabilities through speech recognition and text-to-speech capabilities.
Educational Predictive Analytics: AI analyzes student data to predict future performance and success. Educators can use these predictions to implement targeted interventions and support strategies.
Innovative EdTech Startups: AI has spawned a thriving ecosystem of educational technology startups. These companies develop innovative tools and platforms that cater to a wide range of educational needs, from language learning to virtual labs.
In conclusion, AI has become an indispensable tool in education, offering solutions that enhance personalization, efficiency, and accessibility. As AI continues to advance, it holds the promise of transforming education further, enabling educators and students to achieve better outcomes and adapt to the evolving demands of the digital age. With responsible implementation and a focus on ethical considerations, AI in education has the potential to shape a brighter and more inclusive future for learners of all ages and backgrounds.
E-Learning

E-Learning, or electronic learning, has emerged as a transformative innovation in education, leveraging technology to make learning more accessible, flexible, and effective. This digital approach has significantly impacted the way students acquire knowledge and skills, both in formal and informal settings.
Online Courses and Platforms: E-Learning offers a vast array of online courses and platforms, enabling students to access educational content from anywhere with an internet connection. Renowned universities and institutions provide Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) on a wide range of subjects, democratizing access to high-quality education.
Blended Learning: Blended learning combines traditional classroom teaching with online components, fostering a more interactive and personalized learning experience. Students can access digital resources, engage in discussions, and complete assignments online, complementing in-person instruction.
Mobile Learning: With the proliferation of smartphones and tablets, mobile learning has become increasingly popular. Mobile apps and platforms provide learners with on-the-go access to educational materials, making learning more flexible and convenient.
Virtual Classrooms: Virtual classrooms facilitate real-time, interactive learning experiences. Students and teachers can connect via video conferencing, chat, and collaborative tools, bridging geographical barriers and creating global learning communities.
Self-Paced Learning: E-Learning accommodates diverse learning styles and paces. Students can progress through courses at their own speed, revisiting challenging topics or accelerating through familiar ones, ensuring a tailored learning experience.
Interactive Multimedia: E-Learning materials often incorporate multimedia elements like videos, animations, and simulations, enhancing engagement and comprehension. Complex concepts can be conveyed more effectively through interactive media.
Immediate Feedback: E-Learning platforms provide instant feedback on assessments and quizzes, allowing students to identify areas for improvement and reinforcing their understanding of the material.
Global Accessibility: E-Learning transcends geographic boundaries, making education accessible to individuals in remote or underserved regions. It empowers learners who might not have access to traditional educational institutions.
Cost Efficiency: E-Learning often reduces the costs associated with traditional education, such as commuting, textbooks, and classroom materials. This affordability broadens access to education.
Customization and Personalization: E-Learning platforms use data analytics and AI to personalize learning experiences. They adapt content and assessments based on individual progress and preferences, maximizing learning outcomes.
Professional Development: E-Learning extends beyond formal education to include professional development opportunities. Employees can access training modules and certifications to enhance their skills and career prospects.
In conclusion, E-Learning has reshaped the education landscape, making learning more inclusive, convenient, and adaptable to the needs of learners in the digital age. Its versatility and accessibility continue to play a pivotal role in addressing the evolving demands of education and training, offering a promising path for lifelong learning and skill development. As technology continues to advance, E-Learning is poised to remain at the forefront of educational innovation, shaping the future of learning worldwide
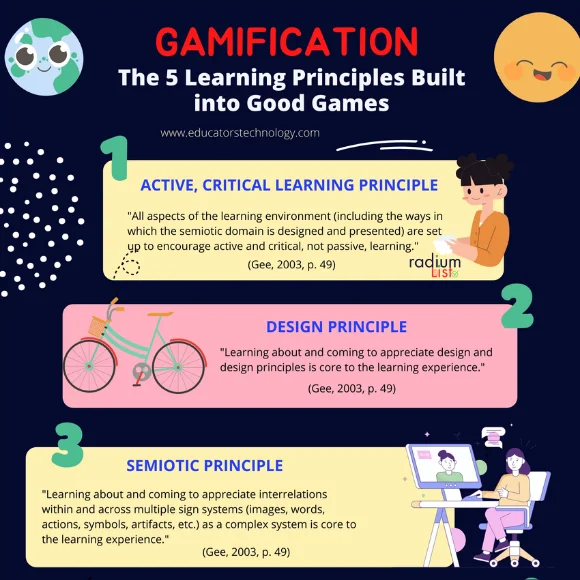
Gamified Learning
Gamified learning, a progressive educational approach, incorporates elements of game design and mechanics into the learning process. It has gained prominence in recent years as a highly engaging and effective way to motivate and educate students across various age groups. Here are some key aspects and benefits of gamified learning:
Engagement and Motivation: Gamification makes learning enjoyable by incorporating game elements such as points, rewards, leaderboards, and challenges. This motivates students to actively participate in lessons and fosters a sense of achievement and competition.
Problem-Solving Skills: Games often present learners with complex challenges and puzzles, encouraging them to think critically and develop problem-solving skills. These skills are transferable to real-life situations.
Adaptive Learning: Gamified platforms can adapt to individual learner abilities. As students progress, the difficulty level of the game or content can adjust accordingly, ensuring an optimal learning experience for each student.
Immediate Feedback: Gamification provides instant feedback on performance. Learners can quickly see the consequences of their decisions in a game, allowing them to make corrections and learn from their mistakes.
Retention and Memory: Gamified learning often utilizes storytelling and immersive narratives, which are known to enhance information retention and memory recall. Learners remember facts and concepts better when embedded in a compelling narrative.
Collaboration and Social Learning: Many gamified learning environments incorporate collaborative elements. Students can work together, solve problems collectively, and learn from their peers, fostering teamwork and social skills.
Autonomy and Self-Directed Learning: Gamification often gives learners a degree of control over their learning journey. This autonomy empowers students to set goals, make choices, and take ownership of their education.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: Gamified learning can be tailored to suit various learning styles and needs, making it accessible to a diverse range of students, including those with learning disabilities.
Real-World Applications: Gamified learning often simulates real-world scenarios, allowing learners to apply knowledge and skills in practical contexts. This bridges the gap between theory and practice.
Data-Driven Insights: Gamification platforms collect data on student performance and behavior. Educators can use this data to gain insights into individual and group learning trends, allowing for more targeted instruction.
Continuous Improvement: Gamification’s iterative nature encourages learners to retry challenges and aim for higher scores, promoting a growth mindset and the idea that effort leads to improvement.
In conclusion, gamified learning represents a dynamic and effective innovation in education. By leveraging the motivational power of games, educators can create engaging learning experiences that enhance student participation, foster critical thinking, and cultivate a lifelong love of learning. As technology continues to advance, gamification in education will likely play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of learning worldwide.
Big Data & Analytics

In the digital age, the education sector is harnessing the power of big data and analytics to revolutionize the way educators teach and students learn. This innovation involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of vast amounts of data to gain valuable insights into student performance, curriculum effectiveness, and institutional decision-making. Here’s how big data and analytics are transforming education:
Personalized Learning: Big data allows educators to create personalized learning paths for students. Analyzing student performance data helps identify individual strengths and weaknesses, enabling tailored content and support to meet each student’s needs.
Early Intervention: By monitoring student progress in real-time, educators can identify at-risk students and intervene early to provide additional support. Predictive analytics can identify potential issues before they impact learning outcomes.
Curriculum Enhancement: Data analytics help institutions assess the effectiveness of their curriculum and teaching methods. It enables continuous improvement by identifying areas where adjustments are needed to better align with learning goals.
Resource Allocation: Schools and universities can optimize resource allocation based on data-driven insights. This includes faculty workload, classroom utilization, and budget allocation for maximum efficiency.
Admission and Enrollment: Big data helps streamline the admission process by analyzing applicant data to predict success and match students with programs that align with their interests and abilities.
Retention and Graduation Rates: Predictive analytics can forecast student retention and graduation rates, allowing institutions to implement strategies to improve student success and reduce dropout rates.
Quality Assurance: Data analytics can be used for quality assurance and accreditation processes, ensuring educational institutions meet established standards and benchmarks.
Teacher Development: Educators can benefit from data-driven insights into their teaching methods. This feedback allows teachers to adapt and refine their instructional approaches to enhance student learning.
Digital Learning Platforms: Online learning platforms utilize data analytics to track student engagement and progress, providing recommendations for content customization and adaptive learning.
Learning Analytics Dashboards: Educational institutions use interactive dashboards to visualize data, making it easier for administrators, educators, and students to track performance and make informed decisions.
Ethical Considerations: As with any application of data, privacy and security are paramount. Educational institutions must ensure the ethical collection and handling of student data to protect individual privacy rights.
In conclusion, big data and analytics have ushered in a new era of data-driven decision-making and personalized learning in education. By leveraging data insights, educational institutions can enhance the learning experience, improve student outcomes, and create more efficient and effective teaching environments. As technology and data analytics continue to evolve, the education sector is poised to benefit from increasingly sophisticated and tailored approaches to teaching and learning.
Personalized Learning
Personalized learning is a transformative innovation in education that shifts away from the one-size-fits-all model of teaching and embraces an approach that tailors education to the unique needs, interests, and pace of each student. This student-centric methodology leverages technology, data, and innovative teaching practices to create highly individualized learning experiences.
Key Elements of Personalized Learning:
Data-Driven Insights: Personalized learning starts by collecting and analyzing data on students’ learning patterns, strengths, and areas needing improvement. This data guides educators in designing customized learning pathways.
Adaptive Content: Adaptive learning platforms use algorithms to adjust the difficulty and content of lessons in real-time based on a student’s performance. This ensures that learners are neither bored nor overwhelmed.
Self-Paced Learning: Personalized learning often allows students to progress at their own pace. They can spend more time on challenging topics while breezing through areas where they excel.

Varied Learning Resources: Students have access to a variety of resources, including digital content, textbooks, videos, and hands-on activities. This diversity allows learners to choose resources that resonate with their learning styles.
Choice and Autonomy: Learners are given choices in how they demonstrate their understanding of a subject. They might create a project, write an essay, or take a traditional test based on their preferences.
Benefits of Personalized Learning:
Improved Engagement: Personalized learning taps into students’ interests and motivations, making learning more engaging and enjoyable.
Enhanced Retention: When students have a say in their learning, they are more likely to remember and apply what they’ve learned.
Better Outcomes: Personalized learning has been associated with improved test scores and academic achievement.
Self-Directed Learning: It fosters the development of essential skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, and self-motivation.
Inclusivity: Personalized learning can address diverse learning needs, making it more inclusive for students with disabilities or those needing additional support.
Preparation for Future: Customized learning experiences prepare students for a future that requires adaptability and lifelong learning.
Challenges:
Technology Integration: Implementing personalized learning often requires a robust technology infrastructure, which can be challenging for some institutions.
Teacher Training: Educators need training to effectively implement personalized learning, as it requires a shift in teaching methods.
Data Privacy: Collecting and using student data for personalized learning must be done carefully to ensure privacy and security.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology, originally designed for secure and transparent cryptocurrency transactions, has found a new application in education. It is revolutionizing how educational institutions manage records, verify credentials, and enhance the overall trustworthiness of academic achievements.
Key Applications of Blockchain in Education:
Credential Verification: Blockchain offers a secure and tamper-proof way to store and verify academic credentials, such as degrees, certificates, and transcripts. These digital records can be easily accessed and shared with employers, institutions, or other parties, streamlining the verification process.
Micro-Credentials and Badges: Blockchain enables the creation and validation of micro-credentials and digital badges for specific skills and achievements. These can be particularly useful for lifelong learners, providing a more granular and comprehensive view of an individual’s abilities.
Academic Records Management: Blockchain simplifies academic record-keeping for institutions, reducing administrative overhead and the risk of errors. All records are securely stored and can be accessed when needed.

Authentication of Online Courses: Educational platforms and MOOCs can use blockchain to verify the authenticity of online courses, ensuring that students receive quality education.
Decentralized Learning Platforms: Blockchain can facilitate the creation of decentralized, peer-to-peer learning networks, enabling individuals to connect and share knowledge without the need for intermediaries.
Transparent Donation Tracking: Educational institutions and nonprofits can use blockchain to track donations transparently, ensuring that funds are used for their intended educational purposes.
Benefits of Blockchain in Education:
Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature and encryption make it highly secure against fraud and data breaches.
Data Integrity: Records stored on a blockchain are immutable, ensuring the accuracy and authenticity of academic credentials.
Accessibility: Students have greater control over their academic records and can easily share them with employers and other educational institutions.
Efficiency: Blockchain streamlines administrative processes, reducing paperwork and the time required for credential verification.
Global Recognition: Blockchain enables the universal recognition of credentials, making it easier for students to study and work internationally.
Challenges:
Integration: Implementing blockchain in education systems requires collaboration among educational institutions, governments, and technology providers.
Privacy Concerns: Maintaining privacy while ensuring data security on a public blockchain can be challenging. Some solutions use private or consortium blockchains to address this issue.
Technical Expertise: Educational institutions and individuals may need to acquire the technical expertise to use blockchain effectively.
Costs: Developing and maintaining blockchain systems can be expensive, which may limit adoption, especially in smaller institutions.
Cloud Computing

Cloud computing has become a pivotal innovation in education, revolutionizing how institutions and educators deliver content, collaborate, and manage administrative tasks. This technology leverages the power of remote servers and internet connectivity to offer a wide range of benefits to the educational sector.
Key Applications of Cloud Computing in Education:
Online Learning Platforms: Cloud-based Learning Management Systems (LMS) provide educators and students with easy access to course materials, assignments, and collaborative tools from anywhere with an internet connection.
Data Storage and Backup: Educational institutions use cloud storage solutions to securely store and back up large volumes of data, including student records, research, and administrative documents.
Collaborative Tools: Cloud-based collaboration platforms facilitate teamwork among students and educators. Features like real-time document editing and video conferencing enhance communication and project collaboration.
Virtual Labs: Cloud computing allows for the creation of virtual labs, enabling students to conduct experiments and simulations remotely. This is particularly valuable for institutions with limited physical lab resources.
Scalability: Cloud solutions can easily scale to accommodate fluctuations in demand, ensuring that educational resources are available when needed.
Accessibility: Cloud technology promotes accessibility, allowing students to access educational resources and tools from a wide range of devices, including laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Education:
Cost Efficiency: Cloud services eliminate the need for on-premises servers and maintenance, reducing IT costs for educational institutions.
Flexibility: Cloud-based solutions offer flexibility, allowing institutions to adapt quickly to changing educational needs and requirements.
Accessibility: Students and educators can access resources from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote learning and collaboration.
Scalability: Cloud solutions can accommodate the growth of educational institutions without significant infrastructure investments.
Security: Cloud providers often have robust security measures in place, safeguarding sensitive educational data.
Disaster Recovery: Cloud storage solutions offer reliable data backup and disaster recovery options, ensuring that critical educational data is protected.
Challenges:
Privacy Concerns: Storing sensitive student and faculty data in the cloud raises privacy and security concerns. Educational institutions must implement stringent security measures and compliance standards.
Internet Connectivity: Access to cloud-based resources relies on internet connectivity, which can be a limitation in some regions.
Training: Faculty and staff may require training to effectively use cloud-based tools and platforms.
Data Portability: There can be challenges in migrating data to and from cloud providers or switching between providers.
Video-assisted Learning
Video-assisted learning is a powerful and versatile innovation in education that leverages the visual and auditory senses to enhance the teaching and learning process. It involves the use of video content, both recorded and live, to deliver educational material, facilitate engagement, and promote deeper understanding.
Key Aspects and Applications of Video-Assisted Learning:
Online Lectures: Educational institutions, especially in higher education, use video lectures to supplement or replace traditional classroom instruction. These recorded lectures can be accessed by students at their convenience, fostering flexible learning.
Interactive Videos: Interactive video content incorporates quizzes, clickable links, and decision points, allowing learners to actively engage with the material and assess their understanding in real time.

Educational YouTube Channels: Many educators and organizations create educational content on platforms like YouTube. These channels cover a wide range of topics and are accessible to a global audience.
Live Streaming: Live video sessions enable real-time interaction between educators and students, promoting engagement and immediate feedback.
Educational Documentaries: Documentaries and educational films provide a visual and engaging way to explore complex topics, making them particularly valuable in history, science, and social studies.
Benefits of Video-Assisted Learning:
Enhanced Engagement: Video content captures and maintains students’ attention, promoting active participation and improved retention of information.
Visual Learning: Visual aids, such as graphics, animations, and demonstrations, can clarify complex concepts and enhance understanding.
Self-Paced Learning: Video content can be paused, rewound, and rewatched, allowing students to learn at their own pace and revisit challenging sections.
Global Accessibility: Video content can be shared and accessed globally, making high-quality education available to a diverse audience.
Flexible Learning: Video-assisted learning accommodates various learning styles, including visual and auditory learners, and can be integrated into both traditional and online learning environments.
Challenges:
Content Quality: Ensuring the quality of video content is essential for effective learning. Poorly produced videos may hinder comprehension.
Accessibility: Some students may face challenges with access to high-speed internet or appropriate devices for video learning.
Passive Consumption: Excessive passive consumption of video content without active engagement can lead to shallow understanding.
Data Consumption: Streaming video content can consume significant amounts of data, which may be a concern for students with limited data plans.
Copyright Issues: Educators and institutions must be mindful of copyright regulations when using video content in teaching.
IoT

The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming education by introducing smart, connected devices and systems that enhance the teaching and learning experience. IoT in education leverages the power of interconnected technology to create more efficient and effective learning environments.
Key Applications of IoT in Education:
Smart Classrooms: IoT-enabled devices such as interactive whiteboards, smart projectors, and digital textbooks create interactive and dynamic learning spaces. Teachers can use IoT to engage students and deliver content in innovative ways.
Campus Security: IoT-based security systems enhance campus safety through smart access control, surveillance cameras, and real-time monitoring. These systems provide a secure learning environment for students and staff.
Student Attendance and Tracking: IoT solutions automate attendance tracking and student location monitoring, reducing administrative tasks and enhancing security. Wearable devices and smart ID cards can help track students on campus.
Energy Efficiency: IoT sensors can monitor and optimize energy consumption in educational facilities. Smart lighting and HVAC systems adjust based on occupancy, reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
Asset Management: IoT helps manage and locate educational resources, including books, equipment, and supplies, efficiently. This reduces resource wastage and saves time in tracking.
Personalized Learning: IoT devices collect data on students’ learning habits and preferences, enabling educators to tailor content and teaching methods to individual needs.
Benefits of IoT in Education:
Enhanced Learning Experience: IoT technology makes learning more interactive, engaging, and personalized, fostering deeper understanding and retention of information.
Efficiency and Cost Savings: IoT optimizes resource utilization, reduces energy costs, and streamlines administrative processes, resulting in financial savings for educational institutions.
Data-Driven Insights: IoT-generated data provides valuable insights into student behavior, campus usage, and facility management, enabling informed decision-making.
Improved Security: IoT enhances campus security through real-time monitoring, emergency response systems, and access control.Environmental Sustainability: IoT solutions contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of educational institutions by optimizing resource consumption.
